Introduction:
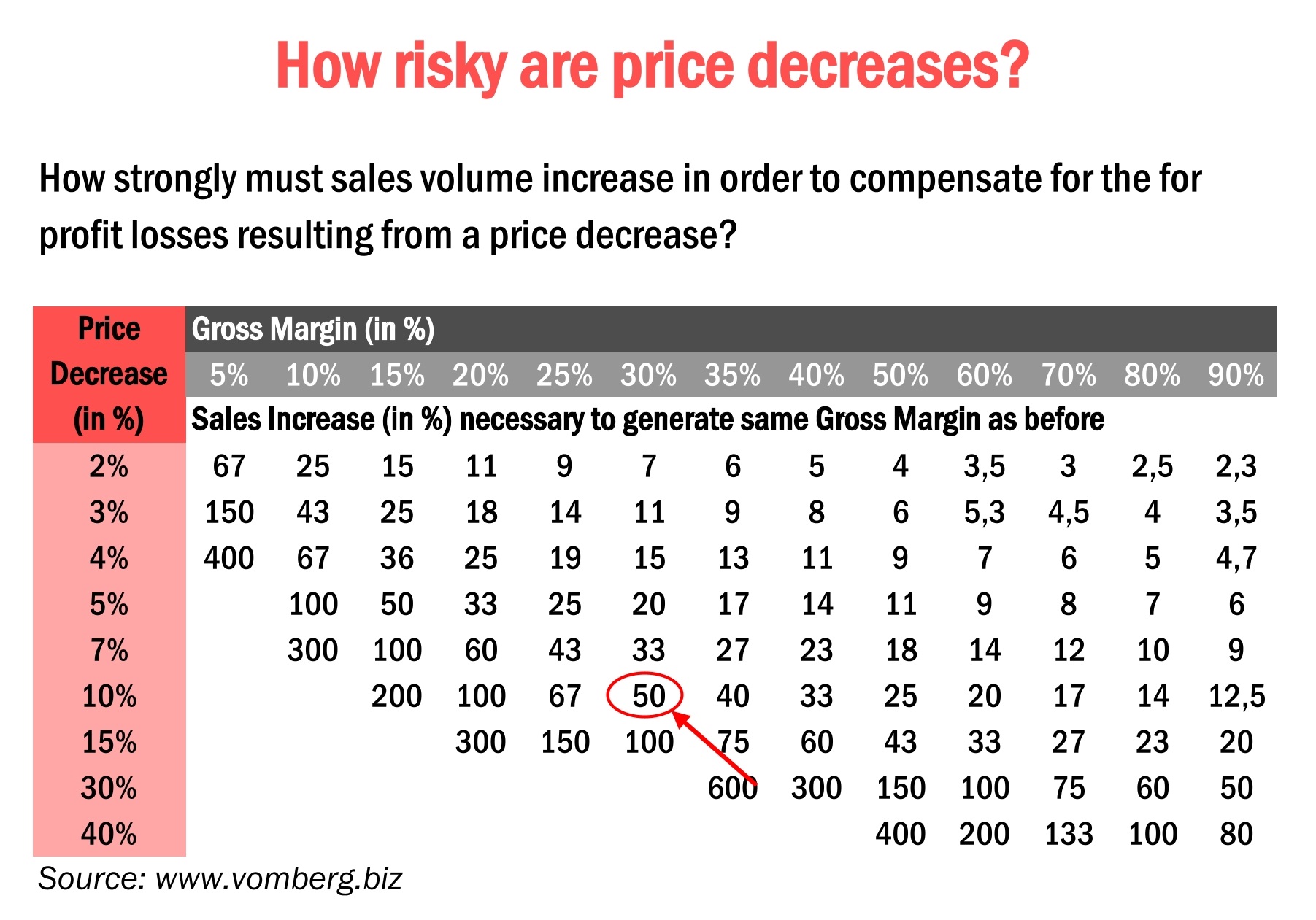
Price decreases can be a powerful tool in attracting customers, but they also come with inherent risks that are often underestimated. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of pricing strategy, exploring the potential dangers of reducing prices, and understanding just how significantly sales volumes must increase to compensate for profit losses resulting from a price cut. To illustrate these risks, we’ll consider a hypothetical example of a company with a gross margin of 30% facing a price decrease by only 10% initiated by a marketing campaign.
The Scenario:
Imagine a company that manufactures electronic devices, and their main product has a gross margin of 30%. The marketing department proposes an awareness campaign that includes a special discount of 10%. This discount seems like a tempting strategy to attract new customers and increase sales volume. However, let’s examine the hidden risks involved.
The Risky Business of a 10% Price Decrease:
On the surface, a 10% discount might seem like a modest reduction, but it can have significant implications for the company’s profitability. Here’s a breakdown of the risks:
- Impact on Profit Margins: A 10% price decrease directly affects the company’s gross margin. In this case, the gross margin is reduced from 30% to 22%, resulting in a 10% decrease in profitability for each unit sold at the discounted price.
- Increased Sales Volume Requirement: To compensate for the profit losses resulting from the price decrease, the sales department needs to sell 50% more devices at the discounted price compared to the original price. This is a substantial increase in sales volume.
Example Calculation:
Let’s put this into perspective with a simplified numerical example:
- Original Price per Device: $100
- Original Gross Margin (30%): $30
After the 10% price decrease:
- Discounted Price per Device: $90
- New Gross Margin (22,2%): $20
To maintain the same level of profit as before the price decrease, the company needs to sell:
- Original Profit per Device: $30
- New Profit per Device: $20
- Required Sales Volume Increase (to compensate for the 10% discount): 50%
The Message:
The message here is clear: a seemingly modest 10% price decrease can result in a significant profit reduction, requiring a substantial increase in sales volume to compensate. This risk is often underestimated, especially for products or services with small profit margins.
The Importance of Awareness:
Awareness of the risks associated with price decreases is crucial for businesses, especially when dealing with products or services that operate on thin profit margins. It’s not just about increasing sales; it’s about balancing increased sales with profit margins to ensure the long-term financial health of the company.
Alternative Strategies:
Instead of relying solely on price decreases, companies can explore alternative strategies to attract customers and boost sales while preserving profit margins. These may include:
- Value-Added Services: Offering additional services or features that enhance the product’s value without compromising price.
- Bundling: Creating product bundles that encourage customers to purchase related items together, increasing the average transaction value.
- Customer Loyalty Programs: Rewarding loyal customers with discounts, exclusive offers, or loyalty points that can be redeemed for future purchases.
- Cross-Selling and Upselling: Encouraging customers to explore complementary or higher-end products during the purchase process.
Conclusion:
Price decreases can be an effective marketing strategy, but they come with hidden risks that can erode profit margins and require substantial sales volume increases to compensate. It’s crucial for businesses to approach price reductions with caution, especially for products or services with narrow profit margins. Awareness of these risks is essential for making informed decisions and balancing the pursuit of increased sales with the preservation of profitability. In the world of pricing strategy, finding the right balance is the key to long-term financial success.